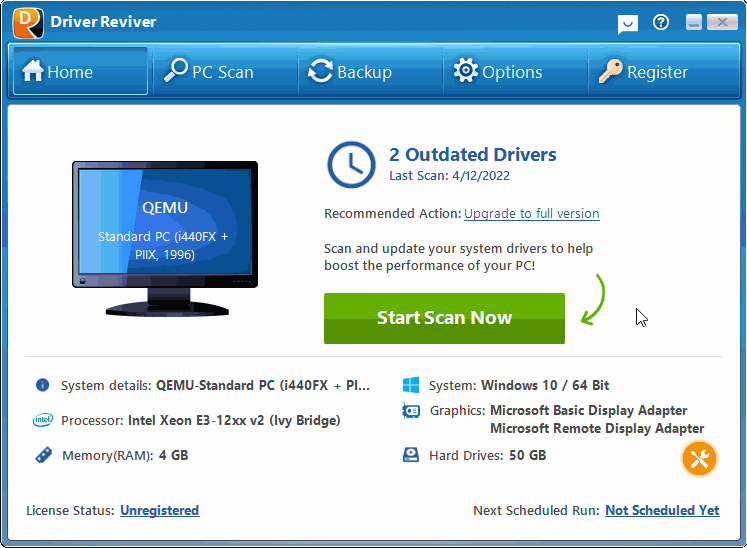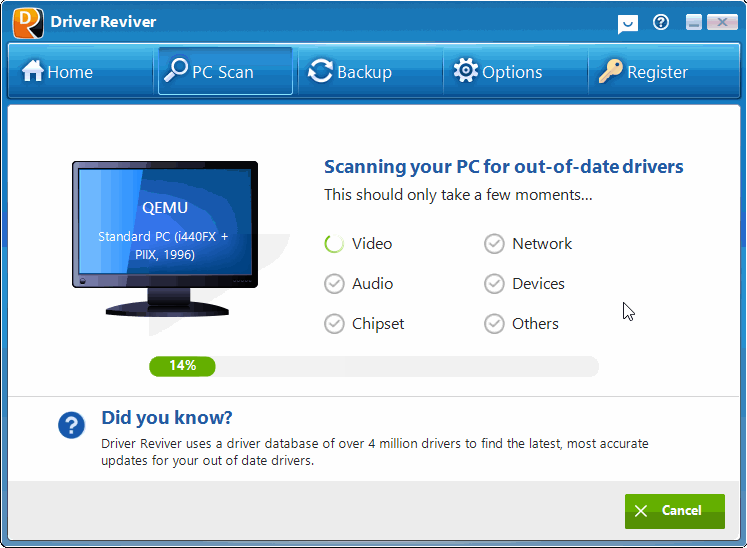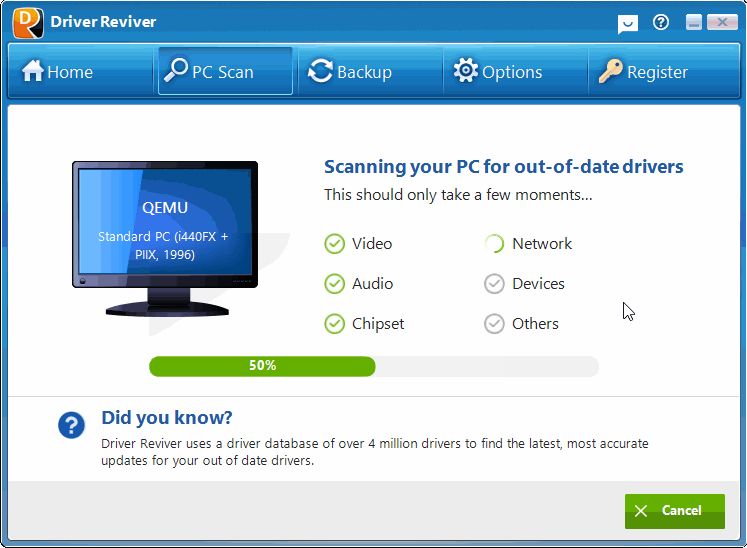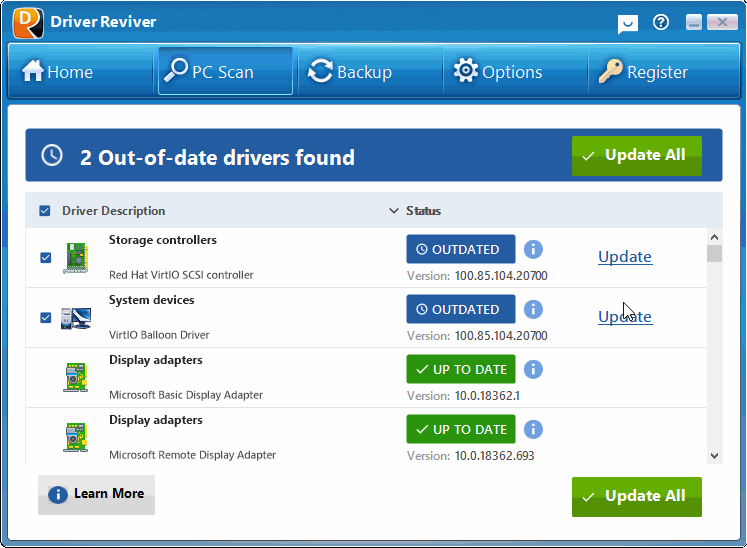
The CACHE_MANAGER BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) error may appear during the initialization process for Windows Vista, XP, and 2000, and Windows 7 and 8. It occurs when the nonpaged pool memory space is depleted. The error results in the automatic shutdown of the computer to prevent damage and possible loss of data from unsaved work.
This error also appears during the indexing process when the available nonpaged pool memory is low and a kernel-mode driver requires its use. The nonpaged pool memory consists of virtual memory addresses that remain in the physical memory while the corresponding kernel objects are allocated.
The CACHE_MANAGER BSOD error may also appear when you burn a Live File System (LFS) formatted disc on a computer that is running Windows 7and 8, or Windows Server 2012. The error is caused by corrupted entry written into the disc when burning data to the optical media. It is usually caused by a bug in the Udfs.sys driver.
This BSOD error is also known as “CACHE_MANAGER” and “STOP 0x00000034“. Some users of Windows have reported this error, which normally appears on the screen during the initialization of the system as:
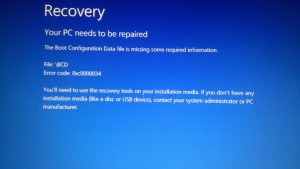
You can resolve the CACHE_MANAGER BSOD error by the addition of physical memory to the computer, which will effectively increase the amount of nonpaged pool memory. The nonpaged memory pool is used by many drivers because it can be accessed at any Interrupt Request Level (IRQL), and its size is dependent on the amount of physical memory present in the system.
The BSOD error that pertains to the faulty operation of the Udfs.sys driver can be addressed by installing the software updates for Windows 7 and 8, and Windows Server 2012.