Chronic disease management is a new way to think about how you manage your patients with chronic illnesses. It’s not just about managing their symptoms or helping them cope with the impact of their disease. It’s about using a patient-centred approach, which focuses on helping people live well and as independently as possible. These are important goals that everyone can strive for.
And it doesn’t have to be hard or time-consuming—you just need an organized plan, a team of support and the right resources in place. In this blog post, we explain what chronic disease management is and how it works. Let’s take a look at some examples of chronic condition management practices, explore its benefits and limitations, and outline some ways you can start implementing this practice in your practice.
Table of Contents
- What is Chronic Disease Management?
- Why use chronic disease management?
- Key benefits of implementing chronic disease management practices
- Limitations of using chronic disease management practices
- How to start doing Chronic Disease Management in your practice
- Conclusion
What is Chronic Disease Management?
Chronic disease management is a new way to think about how you manage your patients with chronic illnesses. It’s not just about managing their symptoms or helping them cope with the impact of their disease. It’s about using a patient-centred approach, which focuses on helping people live well and as independently as possible. These are important goals that everyone can strive for.
And it doesn’t have to be hard or time-consuming—you just need an organized plan, a team of support and the right resources in place. Chronic disease management is a framework for health care delivery that uses a patient-centred, interdisciplinary approach to help people with chronic illnesses live well and stay healthy over time. It’s not just about managing symptoms or helping people cope with the impact of their disease. It’s about helping people live well and as independently as possible.
Why use chronic disease management?
People with chronic conditions face a number of additional health challenges beyond the presence of their condition. For example, they may have additional health risks, such as poor diet and lack of physical activity. They also may have co-existing conditions, such as depression, anxiety, or pain. And they may have social challenges, such as difficulty accessing transportation to medical appointments or finding reliable and affordable care.
 Source : Google Images
Source : Google Images
Chronic disease management aims to address these issues by focusing on people’s health and well-being in addition to their disease. It provides an organized framework for helping patients manage their entire health picture—from their medical condition to the social and economic factors that affect their quality of life. Managing chronic conditions doesn’t just mean treating symptoms and reducing pain. It means helping people live well and as independently as possible.
Key benefits of implementing chronic disease management practices
They can help patients better manage their health conditions. People with chronic diseases may experience long-term health outcomes such as pain, disability, and reduced quality of life. It’s important to help people live well, even with complicated chronic conditions such as arthritis or asthma. They can help improve the quality of life.
People with some chronic conditions, such as arthritis or asthma, report better quality of life when they have access to resources and support that enable them to live well. They can help reduce healthcare costs. People with chronic conditions are more likely to visit the doctor, hospital, and other healthcare providers than those without such conditions. It’s important to manage this chronic disease care in an efficient manner to reduce unnecessary health care costs.
Limitations of using chronic disease management practices
It’s not a one-size-fits-all approach. Chronic disease management is a flexible framework for helping people manage their health. That means you can tailor it to the needs of the person you’re seeing and their family, friends, and community. It also means you’ll have to use your judgment and expertise to assess what’s best for your patient. It can be challenging to get patients to commit to it.
Many people are eager to get their health back on track as soon as possible. And they may not feel like they have enough time to make changes to their health and lifestyle. In these cases, you may want to look at using more urgent-focused care models such as primary care urgent care.
How to start doing Chronic Disease Management in your practice
Begin by identifying the patients you see with chronic conditions. Next, create a list of the resources they need to help manage their health. For example, they may need health insurance, transportation, reliable care, or social support. Engage with these patients by making sure they understand their conditions, their treatment, their symptoms, and the resources they need to live well and stay healthy. This will help you begin to implement chronic disease management practices in your practice. Use a patient-centred approach.
 Source : Google Images
Source : Google Images
This approach is patient-centred because it focuses on helping people live well and as independently as possible. It’s a holistic model that uses medical evidence, patient values and preferences, and skills and knowledge to provide care. Use an interdisciplinary team. Interdisciplinary teams provide a collaborative framework for healthcare delivery that includes physicians, nurses, social workers, dietitians, psychologists, and others. Have a communication plan in place. Communication plans are designed to help patients understand their conditions, treatment options, and resources they need to live well.
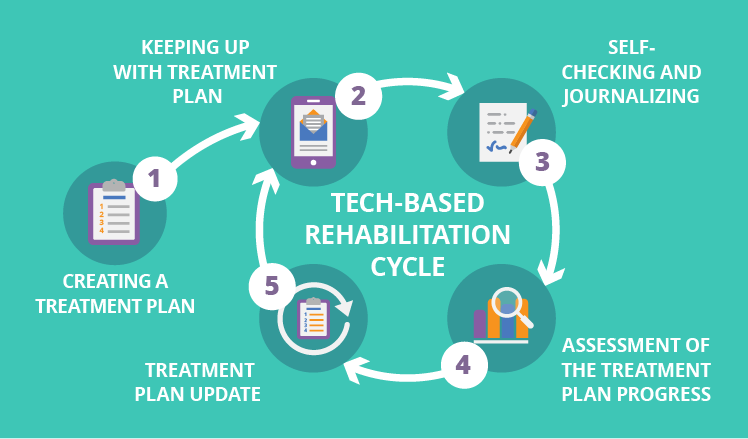
A communication plan may include frequent reminders, written materials, or a video. Explore ways to use technology. Patients with certain conditions may be interested in using technology to track their health, receive treatment reminders, or engage with supportive services.
Conclusion
Chronic disease management is a new way to think about how you manage your patients with chronic illnesses. It’s not just about managing their symptoms or helping them cope with the impact of their disease. It’s about using a patient-centred approach, which focuses on helping people live well and as independently as possible. These are important goals that everyone can strive for.
And it doesn’t have to be hard or time-consuming—you just need an organized plan, a team of support and the right resources in place. Chronic disease management aims to improve a patient’s health and quality of life by helping them manage their entire health picture—from their medical conditions to the social and economic factors that affect their quality of life. Managing chronic conditions doesn’t just mean treating symptoms and reducing pain. It means helping people live well and as independently as possible.





